Operators in JAVA
- Operators are used to operate on data/identifiers (variables)/literals (data/values).
- Operators are intended to change/manipulate the value or used to compare the value with other values.
- identifier: int i=10; i is a int identifier/int variable name
- literal: means value. 10 is int literal, true is Boolean literal, "Abdul" is String literal.
- Operators are used to operate on variables and values. They are intended to modify the values or compare one variable value with other variable value.
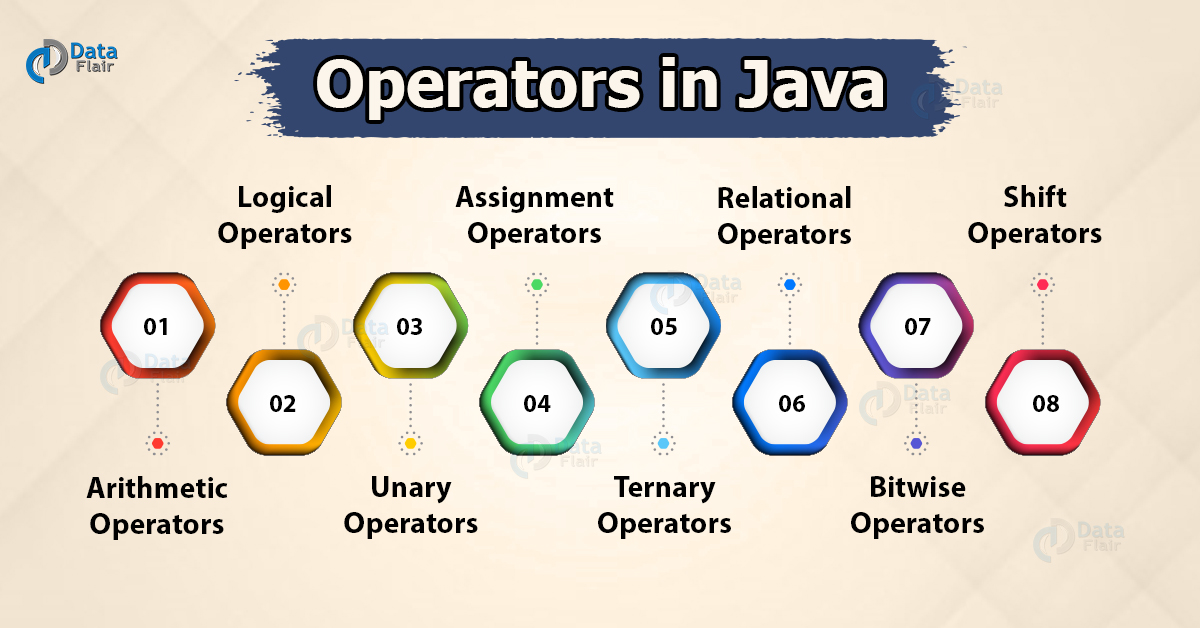
Top-Level: Arithmetic, Assignment, Prefix/Postfix, Logical, Relational, Ternary, Bitwise, Shift
Operators are classified into 3 types:
i) Unary Operators - Operator which operates on a single operand
- Pre Increment-Decrement Operators ++i, --i ++10
- Post increment-Decrement Operators i++, i-- 10--
- Not Operator !flag
- ~ Bitwise NOT ~i
ii) Binary Operators
- Arithmetic Operators a+b, a-b, a*b, a/b, a%b
- Assignment Operators int i=10, i+=10 (or) i=i+10, i-=10, i*=10, i/=10, i%=10
- Logical Operators &, |, ^, &&, ||
- Relational Operators ==, !=, <, <=, >, >=
- Bitwise Operators
- Shift Operators
iii) Ternary Operator/Conditional Operator
- Ternary Operator output=(condition)?lhs:rhs
E.G. : int k=(10>5)?10:5;
// Example on ArithmeticOperatorsTest.java
public class ArithmeticOperatorsTest {
public static void main(String rags[]) {
int i=5, j=2;
int k = i + j;
// 10 + 20 = 30
System.out.println(i+" + "+j+" = "+k);
int l = i - j;
System.out.println(i+" - "+j+" = "+l);
int m=i * j;
System.out.println(i+" * "+j+" = "+m);
int n=i / j;
System.out.println(i+" / "+j+" = "+n);
int o=i % j;
System.out.println(i+" % "+j+" = "+o);
}
}
// Example on OperatorAssignmentTest.java
public class OperatorAssignmentTest {
public static void main(String rags[]) {
int i=10;
i=i+1;
System.out.println("i initial value is 10, i + 1 is = "+i);
int j=10;
j+=1;
System.out.println("j initial value is 10, j += 1 is = "+j);
int k=10;
k=k-1;
System.out.println("k initial value is 10, k - 1 is = "+k);
int l=10;
l-=1;
System.out.println("l initial value is 10, l-=1 is = "+l);
int m=10;
m*=10;
System.out.println("m initial value is 10, m*=10 is = "+m);
int n=10;
n/=10;
System.out.println("n initial value is 10, n/=10 is = "+n);
int o=10;
o%=10;
System.out.println("o initial value is 10, o%=10 is = "+o);
}
}
// PrefixPostfixTest.java
public class PrefixPostfixTest {
public static void main(String rags[]) throws Exception {
int i=25, j=70;
System.out.println("i is "+i); // 25
System.out.println("++i is "+(++i)); // 26
System.out.println("j is "+j); // 70
System.out.println("j++ is "+(j++)); // 70
System.out.println("j is "+j); // 71
int k=25, l=70;
System.out.println("k is "+k); // 25
System.out.println("--k is "+(--k)); // 24
System.out.println("l is "+l); // 70
System.out.println("l-- is "+(l--)); // 70
System.out.println("l is "+l); // 69
}
}
Logical Operators:
- Applied between two conditions / relational operations.
- & Logical AND
- | Logical OR
- ^ Logical XOR
- && Short circuit AND
- || Short circuit OR
// LogicalOperatorsTest.java
public class LogicalOperatorsTest {
public static void main(String rags[]) {
int a=25;
int b=75;
double x=35.87;
double y=67.43;
char c1='b';
char c2='d';
/* Though first condition is false or second condition will be checked, if any one is false, false will be returned. if both are true then true will be return. if both are false, false will be return. */
System.out.println((a>b) & (x<y));
/* if any one condition is true, true will be returned, if both are false, false, if both are true. */
System.out.println((a>b) | (x<y));
/*
if both are true or false, false. If anyone is true and other one is false, true
x^y=x.y'+y.x'
*/
System.out.println((c1==c2) ^ (b>100));
System.out.println((c1==c2) ^ (b==75));
System.out.println((a>b) && (x<y));
System.out.println((a>b) || (x<y));
}
}



0 Comments