OOPs in JAVA
There are some principles which are to be learnt before studying about object oriented programming
in java language. They are called Solid principles
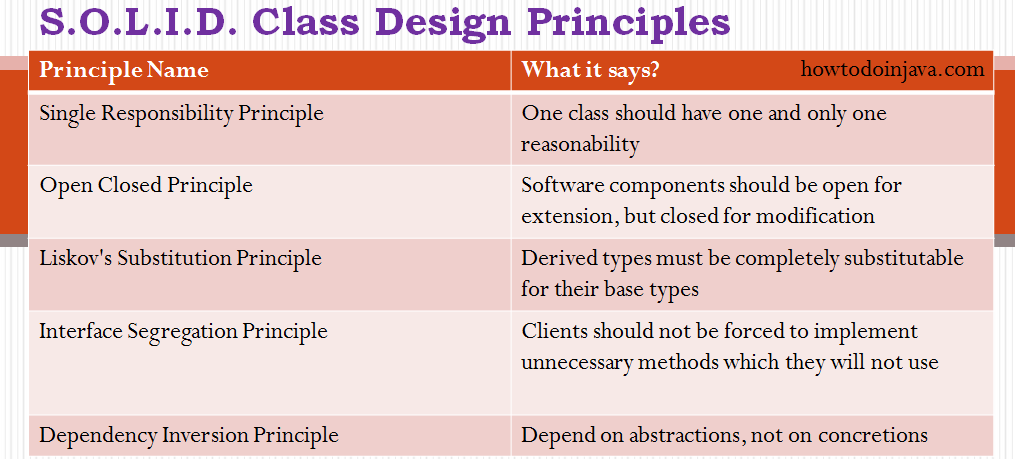
SOLID Principles:
- S Single Responsibility Principle (SRP)
- O Open/Closed Principle (OCP)
- L Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP)
- I Interface Segregation Principle (ISP)
- D Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)
Some important topics about this is oops are Encapsulation, Abstraction, Inheritance, Polymorphism, Message passing (pass by value, pass by reference)
Types of classes: interface, abstract class, class, final class, inner class, anonymous class
All access modifiers (abstract, static, final, transient, volatile, native, synchronized)
super & this are keywords
SOLID Principle:
• Single responsibility principle (SRP): This principle states that a software component (function, class, or module) should focus on one unique task (have only one responsibility).
• Open/closed principle (OCP): This principle states that software entities should be designed with application growth (new code) in mind (should be open to extension), but the application growth should require the fewer possible number of changes to the existing code (be closed for modification).
• Liskov substitution principle (LSP): This principle states that we should be able to replace a class in a program with another class as long as both classes implement the same interface. After replacing the class, no other changes should be required, and the program should continue to work as it did originally.
• Interface segregation principle (ISP): This principle states that we should split interfaces that are very large (general-purpose interfaces) into smaller and more specific ones (many client-specific interfaces) so that clients will only need to know about the methods that are of interest to them.
• Dependency inversion principle (DIP): This principle states that entities should depend on abstractions (interfaces) as opposed to depending on concretion (classes).
Types of Classes we will implement in OOP/Java:
In Java we will write varieties of classes:
i) Java Beans/POJO (Plain Old Java Object)/DTO (Data Transfer Object)/VO (ValueObject)/BO (Business Object)/Entity class/Domain Object.
class Student implements Serializable, Comparable {
private int sid;
private String sname;
private String email;
private long mobile;
private String course;
Student() {}
// parameterized constructor
// pair of setter and getter methods
public int compareTo(Object o) {
Student s=(Student)o;
if(this.sid<s.sid)
return -1;
else if(this.sid>s.sid)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// override equals(), hashCode(), toString()
public boolean equals(Object o) {
boolean flag=false;
if(o instanceof Student) {
Student s1=(Student)o;
if(this.sid==s1.sid && this.sname.equals(s1.sname) && this.email.equals(s1.email) && this.mobile==s1.mobile && this.course.equals(s1.course)) {
flag=true;
}
}
return flag;
}
public String toString() {
return sid+" "+sname+" "+email+" "+mobile+" "+course;
}
// convert variable length String into fixed length integer for faster comparision
public int hashCode() {
return toString().hashCode();
}
public Object clone() {
// deep cloning & shallow cloning
// shallow cloning
// return this;
// deep cloning
Student s1=new Student();
s1.sid=this.sid;
s1.sname=this.sname;
s1.email=this.email;
s1.mobile=this.mobile;
s1.course=this.course;
return s1;
}
}
class Emp implements Serializable, Comparable {
int eid;
String ename;
double sal;
String desig;
}
class Course {
int cid;
String cname;
int duration;
String content;
}
class CourseBatch implements Serializable, Comparable {
int bid;
Course couse;
Faculty faculty;
// Student students[];
List<Student> students;
}
ii) Standalone classes
which contains main() method to run on command prompt
iii) Factory classes
Classes which creates objects of other classes
iv) Validator classes
NotNull, MinLength, MaxLength, Date, Email, URL, CreditCard, PANCard, AadharCardNo, SSNo, ZIP, Pattern/RegExpr validatons
v) Business logic/ Service classes
calSal(), calTaxAmount(), calTotalCartAmount(), calTotalMarks(), calGrade(), calPercentage()
vi) DAO (Data Access Object) classes
To implements JDBC/File IO API to implement CRUD operation
vii) Thread classes
To implement Threads to make multiple methods run simultaneously
viii) Comparable classes
To natural sort objects in collections based on default/PK/ID property
public int compareTo(Object o) {}
ix) Comparator classes
To natural sort objects in collections based on other properties
public int compare(Object lhs, Object rhs) {}
x) Remote classes
RMI, CORBA, EJB, SOAP WebServices, RESTful WebServices
xi) Web Components / Servlet classes
Servlets, JSP classes
xii) Tag Library Classes



0 Comments