Last part of Storage classes
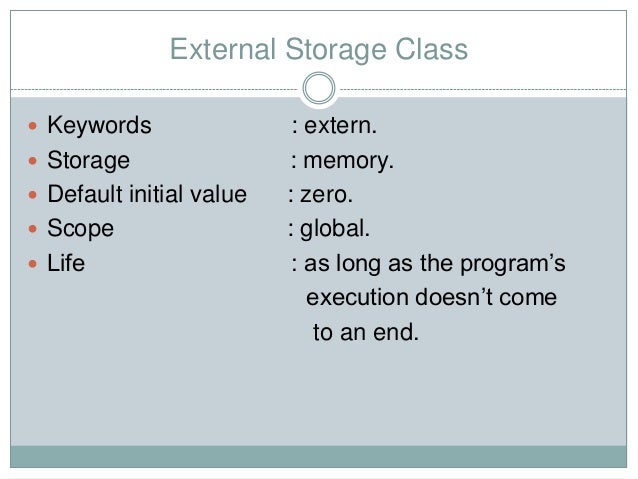
External
storage class:
It is used to declare global variables.
These are linked at the time of creating exe file.
Declaration:
Syntax :
extern int a;
extern int a=10; à invalid
extern variable should not be
initialized.
Program to check scope of the variable.
#include<stdio.h>
/* below is a global variable but not
extern.
Below variable is global to current file only. It can be accessed from
function in the current file.
If it is external variable, then it is global to all files in the
C-Application and it can be accessed at run time from function of any file in
C-Application.
*/
int a=10;
main()
{
printf(“
%d “, a);
f1();
printf(“ %d “, a);
f2();
printf(“ %d “, a);
f1();
printf(“ %d “, a);
f2();
printf(“ %d “, a);
}
f1()
{
int
a=10;
a=a+20;
}
f2()
{
a=a+50;
}
Global variable as static:
#include<stdio.h>
static int
a=10;
main()
{
=========;
=========;
=========;
}
If global variables are declared as
static, it can not be accessed from the linked files.
main intension of this declaration is to
make availability inside the current file only.
Extern variable can be accessed from any
where in the application, including from linked files.



1 Comments
Super Text by Tech channel with Dsk
ReplyDeleteKeep Doing!!