Pointer to array of structures:
struct employee emp[5];
struct employee *ptr;
ptr=emp;à value = base address = 1000
ptr++ è
ptr = ptr+1 à 1000+1*51 = 1051
ptr++ = 1051 + 1*51 = 1102
ptr++ = 1102+1*51 = 1153
ptr++ = 1153 + 1*51 = 1204
For variable way of accessing is by
using dot ( . ) operator
eg:
emp.empNum;
for pointer variable way of accessing is by using arrow ( à
) operator
ptràempNum;
pointer to pointer :
int a=10;
int *ptr1=&a;à pointer to variable
int
**ptr2=&ptr1;à pointer to
pointer.
Eg:
int
a=10;
int *ptr1=&a;
int **ptr2=&ptr1;
printf(“\n
%d “,a); à o/p : 10
*ptr1=20;
printf(“\n
%d “,a); à o/p : 20
**ptr2=30;
printf(“\n %d
“,a); à o/p : 30
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a=10;
int *ptr1=&a;
int **ptr2=&ptr1;
float *fp;
printf("\n%d %u %u ",a,ptr1,ptr2);
printf("\n%u %u
%u",&a,ptr1,*ptr2);
printf("\n%u %u %u ",&ptr1,ptr2,
&ptr2);
printf("\n%d
%d
%d",sizeof(ptr1),sizeof(ptr2),sizeof(fp));
return 0;
}
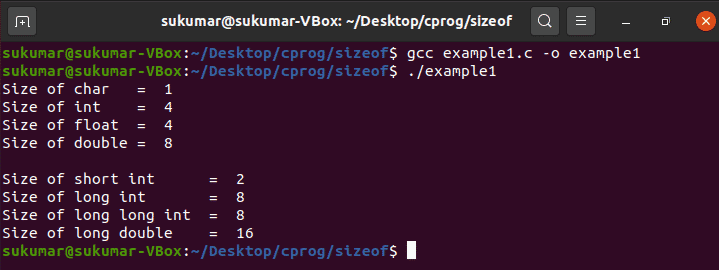
Size of a pointer
1. Size of pointer is
not depending on data type.
2. Pointer contains
address, which is an unsigned int.
3. Since size of unsigned
int is 2 bytes, size of pinter is also 2 bytes.
4. Size of pointer
depends compiler.
5. As per 32 bit
compile size of int is 2 bytes, hence size pointer also 2 bytes.
6. As per 64 bit
compile size of int is 4 bytes, hence size pointer also 4 bytes.
7. Type of the
pointer, gives instruction, how many bytes has to read from the memory.
Program to check size of pointer:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int a=10;
float b=20.5;
char ch='x';
int *ip;
float *fp;
char *cp;
clrscr();
ip=&a;
fp=&b;
cp=&ch;
printf("\n%d %f %c",*ip,*fp,*cp);
printf("\n%d %d
%d",sizeof(ip),sizeof(fp),sizeof(cp));
return 0;
}
Note: All the programs given here are pre compiled and pre runned. If the viewer has any doubt about these they are free to run the compiler provided after each program.



0 Comments