Data types
Their memory, data types ranges, their default values, variable declaration, initialization, type casting and conversions using wrapper classes:
for java classes online refer to the below given link:
And for contacting instructor refer click the link given above
Is Java datatypes are signed datatypes or unsigned datatypes?
Signed datatypes:
C, C++ supports ASCII range characters char ch='A';
Java supports Unicode range characters char ch='A';
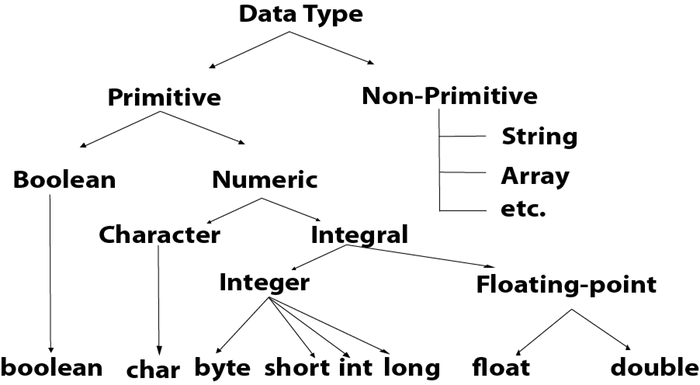
Primitive data types:
Numeric data types:
1. Integer type data types
byte - 1 byte - (-128 to +127), 0
short - 2 bytes - (-32768 to +32767), 0
int - 4 bytes - (-2147483648 to +2147483647), 0
long - 8 bytes, -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 .. 9,223,372,036,854,775,807
2. floating point data types
float - 4 bytes - (-3.402823E38 to +3.402823E38), 0.0f
double - 8 bytes - (-1.79769313486232E308 to +1.79769313486232E308), 0.0d
Character data type:
char - 2 bytes, 0-255 (ASCII), 0-255,256-65535 - 65536 (Unicode), \u000
char ch='a'; 'A' '0' 'Σ'
97 65 48 228
String frml="πΣ¥Ω"
For ASCII range characters in case of language supporting ASCII range chars:
char ch='~'; 126
char ch='¥'; 157 instead -108
For ASCII range characters in case of language supporting Unicode range chars:
char ch='~'; 126
char ch='¥'; 157
Boolean data type
Boolean - 1 byte, (true/false), false
Secondary data types:
arrays - int i[]=new int[10]; i[0]=1; i[9]=10; int j[]={1,2,3,4,5};
classes - class Emp {}, class Student {}, class Customer {}
// DataTypeRangeTest.java
public class DataTypeRangeTest {
public static void main(String rags[]) {
// byte b=-128b; // valid
// byte b=-129;// compilation error, possible loss of precision
// byte b=127B;
// byte b=128;
byte b=127b;
byte b1=127B;
short s=-32768s;
short s1=32767S;
int i=-2147483648i;
// int i1=2147483648; // integer number too large
int i1=2147483647I;
// all integer literals are by default treated as int hence long value must suffix with l or L
long l=-2147483649L;
long l1=2147483648L;
float f=-3.402823E38F;
float f1=+3.402823E38f;
// all floating point literals are by default treated as double hence float value must suffix with f or F
double d=-1.79769313486232E307d;
double d1=1.79769313486232E307D;
char ch='A';
char ch1=65;
boolean boo=true;
}
}



0 Comments